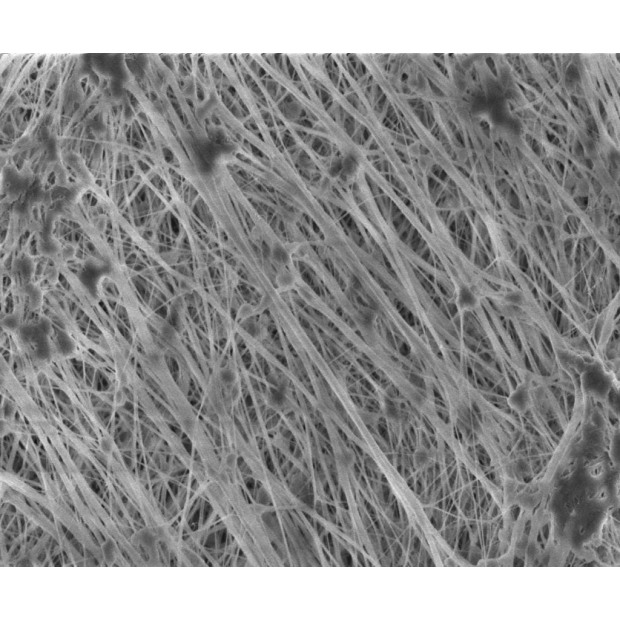
ePTFE Waterproof Membrane Introduction
Preservative
It can withstand the action of all strong acids (including fluoroantimonic acid, aqua regia), strong alkalis, strong oxidizing agents, reducing agents and various organic solvents except molten alkali metals, fluorinated media and molten strong alkalis.
Insulation
Not affected by the environment and frequency, the resistivity can reach 1018 ohm cm, the dielectric loss is small, and the breakdown voltage is high.
Weather resistance
Radiation resistance and low permeability: long-term exposure to the atmosphere, the surface and performance remain unchanged.
Non-flammable
The limiting oxygen index is below 90.
Non-sticky surface
None of the known solid materials can adhere to the surface, and it is a solid material with the smallest surface energy
High and low temperature resistance
The influence on temperature does not change much, and the temperature range is wide, and the usable temperature is -190~260 ℃.
PTFE physical properties
PTFE is a white solid at room temperature with a density of about 2.2 g/cm3. According to DuPont's records, its melting point is 327°C (620.6°F), but it will deteriorate above 260°C (500°F). Its coefficient of friction is less than or equal to 0.1, which is the solid substance with the smallest known coefficient of friction. The mechanical properties of PTFE are relatively soft. Has very low surface energy.
PTFE chemical properties
Corrosion resistance: It can withstand the action of all strong acids (including fluoroantimonic acid, aqua regia), strong alkalis, strong oxidants, reducing agents and various organic solvents except molten alkali metals, fluorinated media and molten strong alkalis.
Insulation: not affected by the environment and frequency, the resistivity can reach 1018 ohm cm, the dielectric loss is small, and the breakdown voltage is high.
High and low temperature resistance: little change in temperature, wide temperature range, usable temperature -190~260 ℃.
Self-lubrication: It has the smallest friction coefficient among plastics and is an ideal oil-free lubricating material.
Non-sticky surface: None of the known solid materials can adhere to the surface, and it is a solid material with the smallest surface energy.
Atmospheric aging resistance, radiation resistance and low permeability: long-term exposure to the atmosphere, the surface and performance remain unchanged.
Non-combustibility: The limiting oxygen index is below 90.
PTFE toxicity
PTFE is non-toxic under normal conditions, but PTFE cooking utensils begin to deteriorate when the temperature reaches 500°F (260°C), and begin to decompose above 660°F (350°C). DuPont stated in "Important Knowledge about Using DuPont Teflon Non-stick Coated Cookware" that inert polytetrafluoroethylene will undergo chemical changes when the temperature reaches 260 °C. In comparison, when cooking oil, fat, and cream, temperatures reaching about 392°F (200°C) will produce charring and smoke, while meat typically chars between 400°F–450°F (200°C–230°C) However, if you place empty cooking utensils on the fire, it is easy to exceed this temperature inadvertently. In a study in 1959 (before the FDA approved the substance for food conditioning appliances), it was shown that coated pans were more toxic in the gases produced when they were dry-boiled (no food in the pan) than when they were cooked. Generally, the toxicity of the gas produced by edible oil is low.